
University of Michigan M-STEM Program
The Guaranteed 4.0 program contributed to the success of underrepresented minority engineering students enrolled in the University of Michigan’s Fall 2008 M-STEM Program. The overall GPA for students enrolled in M-STEM was 3.218, compared with an overall GPA of 3.152 for all College of Engineering students and an overall GPA of 2.833 for underrepresented minority students who did not participate in the M-STEM Program.Proven Track Record
Arizona State University
In the fall of 2003, as part of a five-year block grant, the Fulton School of Engineering began its first National Action Council for Minorities in Engineering (NACME) class for scholars. The third class of freshmen began their studies in the fall of 2005. A major difference for the third cohort was the inclusion of the principles of the Guaranteed 4.0 learning system at the beginning of their freshman year.
University of Maryland
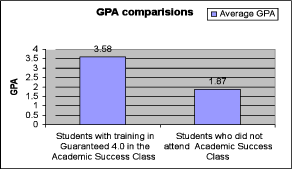
Guaranteed 4.0 learning principles were introduced into the S.T.E.M. program at the University of Maryland. Working with underrepresented minority students, the program saw a dramatic increase in the number of students receiving a 3.0 or greater GPA (18% increase between fall 2006 and spring 2007), and a diminished percent of students receiving a 2.0 GPA or less (17% decrease between fall 2006 and spring 2007—students who effectively left academic probation). There was also a 2.04 GPA difference between students who were on plan 30-40% of the time (1.8 GPA) and students who were on plan 90% of the time (3.84 GPA).
Prominent West Coast Research Institute

A prominent West Coast research institute gave three groups of thirty participants each twenty minutes to read a general purpose article. The “Control” group read the article without any additional action. The “Highlight” group was allowed to highlight, circle and underline while reading. The “BPR” group was given fifteen minutes instruction on how to do BPR, including one practice BPR prior to reading the article. All participants were given a quiz based on the material read. In Test 1a the “Control” and Highlight” group’s test scores averaged 27% while the “BPR” group averaged 77%. For the second test, administered 48 hours following Test 1, the groups were given five minutes to review the same article as in Test 1. The “Control” group reviewed the article without any additional action, while the “Highlight” and “BPR” groups reviewed their own personally notated copies of the article utilized in Test 1. Participants were then given the same quiz as in Test 1 (same content, question order changed). In Test 2 the scores increased to 32% (“Control” group), 25% (“Highlight” group) and 82% (“BPR” group). In both tests there was a noticeable 50% difference between the test scores of the “Control” and “Highlight” groups and the “BPR” group.



